Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes Topics in the Chapter:
- Introduction
- Systems for Control and Coordination in Animals
- Nervous System
- Neuron
- Functioning of Neuron
- Parts of Neuron
- Synapse
- Reflex Action
- Types of Responses
- Need for Reflex Action
- Human Nervous System
- Human Brain
- Fore-Brain
- Mid-Brain
- Hind-Brain
- Protection of Brain and Spinal Cord
- Coordination between Nervous and Muscular Tissue
- Limitation of Electric Communication/Nervous System
- Chemical Combination
- Coordination in Plants
- Independent of Growth
- Dependent on Growth
- Plant Hormones
- Hormones in Animals
- Endocrine Glands and Their Functions
- Importance of Iodine
- Diabetes
- Cause of Diabetes
- Treatment of Diabetes
- Feedback Mechanism
Introduction
- All living organisms respond and react to changes in their environment.
- These changes, known as stimuli, include light, heat, cold, sound, smell, and touch.
- Both plants and animals respond to stimuli but in different ways. Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes
Systems for Control and Coordination in Animals
- Control and coordination in animals are managed by two main systems: Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes
- Nervous System
- Endocrine System
Nervous System
- Control and coordination are provided by nervous and muscular tissues.
- Nervous tissue comprises an organized network of nerve cells or neurons, which conduct information via electrical impulses.
Receptors
- Receptors are specialized tips of some nerve cells that detect information from the environment. Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes
- These are located in sense organs:
- Ear: Phonoreceptors (sound), balance.
- Eyes: Photoreceptors (light), vision.
- Skin: Thermoreceptors (temperature), touch.
- Nose: Olfactory receptors (smell).
- Tongue: Gustatory receptors (taste).
Neuron
- The structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
Functioning of Neuron
- Receptors acquire information as chemical reactions that create electrical impulses.
- Impulses travel from the dendrite to the cell body and then to the axon end.
- Chemicals released at the axon end cross the synapse to start similar impulses in the next neuron. Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes
Parts of Neuron
- Dendrite: Acquires information.
- Cell Body: Transmits impulses.
- Axon: Transmits impulses from the cell body to the next neuron.
Synapse
- A gap between the nerve ending of one neuron and the dendrite of another.
- Converts electrical signals to chemical signals for transmission. Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes
Reflex Action
- Reflex action is a quick, immediate response to a stimulus (e.g., knee jerk, withdrawal from hot objects).
- Reflex arc: Pathway through which nerve impulses pass during reflex action. Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes
- Types of Responses:
- Voluntary: Controlled by the forebrain (e.g., talking, writing).
- Involuntary: Controlled by the mid and hind brain (e.g., heartbeat, respiration).
- Reflex Action: Controlled by the spinal cord (e.g., withdrawal from heat).
Need for Reflex Actions
- Reflex actions provide quick responses to avoid harm, often involving the spinal cord instead of the brain to save time. Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes
Human Nervous System
- Consists of:
- Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain and spinal cord.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Cranial and spinal nerves.
Human Brain
- Main coordinating center with three major parts: Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes
- Fore-brain
- Mid-brain
- Hind-brain
Fore-brain
- The most complex part, consisting of the cerebrum.
- Functions: Thinking, voluntary actions, memory, sensory integration, hunger.
Mid-brain Control and Coordination Class 10 Notes
- Controls involuntary actions like pupil size and reflex movements.
Hind-brain
- Composed of:
- Cerebellum: Posture, balance, precision in voluntary actions.
- Medulla: Involuntary actions (e.g., blood pressure, vomiting).
- Pons: Regulation of respiration.
Protection of Brain and Spinal Cord
- Brain: Protected by a fluid-filled balloon (shock absorber) within the cranium.
- Spinal Cord: Enclosed in the vertebral column.
Coordination between Nervous and Muscular Tissue
- Voluntary actions require brain signals to muscles.
- CNS and PNS facilitate communication throughout the body.
Limitations of Electric Communication/Nervous System
- Limited to cells connected by nervous tissue.
- Cells need time to reset before transmitting another impulse.
- Plants lack a nervous system.
Chemical Communication
- Overcomes limitations of electric communication through hormones.
Coordination in Plants
- Types of Movements:
- Independent of Growth: Immediate responses (e.g., touch-me-not plant).
- Dependent on Growth: Directional movements (tropism) like phototropism, geotropism, chemotropism, and hydrotropism.
Plant Hormones
- Chemical compounds coordinating growth and responses.
- Main hormones:
- Auxin: Growth towards light.
- Gibberellin: Stem growth.
- Cytokinins: Cell division.
- Abscisic Acid: Growth inhibition, stress response.
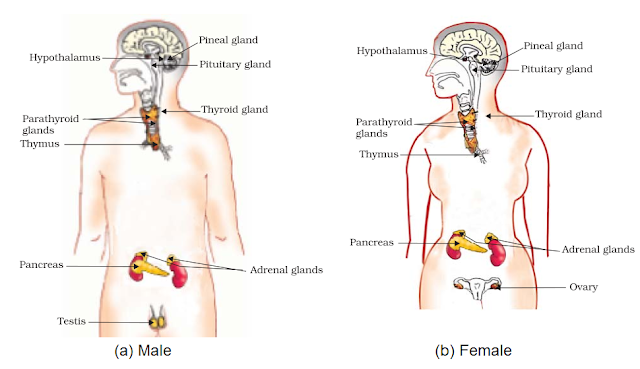
Hormones in Animals
- Endocrine Glands: Secrete hormones into the blood.
- Key hormones and functions:
- Thyroxine (Thyroid): Metabolism regulation.
- Growth Hormone (Pituitary): Growth and development.
- Adrenaline (Adrenal): Emergency responses.
- Insulin (Pancreas): Blood sugar regulation.
- Sex Hormones: Puberty changes (testosterone, estrogen).
Importance of Iodine
- Essential for thyroxine production (metabolism regulation).
- Deficiency causes goiter (swollen neck).
- Cause: Insulin deficiency.
- Treatment: Insulin injections.
Feedback Mechanism
- Ensures precise hormone secretion to avoid harmful effects.
- Example: Blood sugar regulation by insulin.
You might also check these ralated posts.....